What kind of products are capacitors and capacitors?
What Kind of Products are Capacitors and Capacitors?
I. Introduction
Capacitors are essential components in the world of electronics, playing a crucial role in various applications ranging from simple circuits to complex systems. Defined as passive electrical devices that store and release electrical energy, capacitors are integral to the functionality of many electronic devices. Their ability to store energy temporarily makes them invaluable in smoothing out voltage fluctuations, filtering signals, and timing applications. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of capacitors, their types, applications, market products, challenges, and future trends.
II. Understanding Capacitors
A. Basic Principles of Capacitance
At the heart of every capacitor is the principle of capacitance, which is defined as the ability of a component to store an electrical charge. Capacitance is measured in farads (F), and it represents the amount of charge a capacitor can hold per volt of electrical potential. When a voltage is applied across a capacitor, it accumulates charge on its plates, creating an electric field that stores energy. This stored energy can be released when needed, making capacitors vital for various electronic functions.
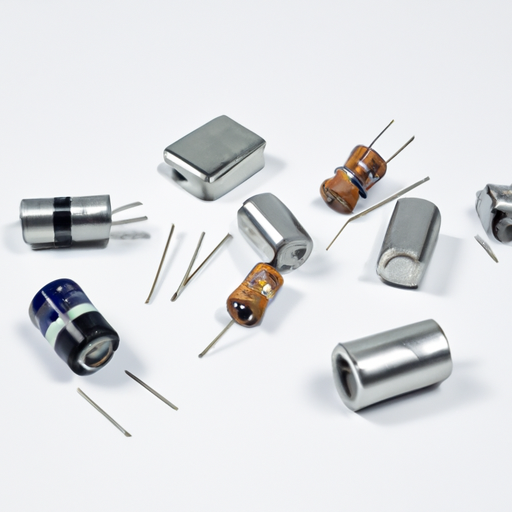
B. Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in various types, each designed for specific applications and characteristics:
1. **Electrolytic Capacitors**: Known for their high capacitance values, electrolytic capacitors are polarized devices that use an electrolyte to achieve greater capacitance. They are commonly used in power supply circuits for smoothing and filtering.
2. **Ceramic Capacitors**: These capacitors are made from ceramic materials and are non-polarized. They are widely used in high-frequency applications due to their stability and low losses.
3. **Film Capacitors**: Constructed from thin plastic films, these capacitors are known for their reliability and stability. They are often used in audio applications and power electronics.
4. **Tantalum Capacitors**: Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small package and are used in applications where space is limited, such as in mobile devices.
5. **Supercapacitors**: Also known as ultracapacitors, these devices can store large amounts of energy and are used in applications requiring rapid charge and discharge cycles, such as in renewable energy systems.
C. Key Specifications and Ratings
When selecting a capacitor, several key specifications must be considered:
1. **Capacitance Value**: This indicates the amount of charge the capacitor can store and is typically expressed in microfarads (µF) or picofarads (pF).
2. **Voltage Rating**: The maximum voltage the capacitor can handle without breaking down. Exceeding this voltage can lead to failure.
3. **Tolerance**: This specification indicates how much the actual capacitance can vary from the stated value, usually expressed as a percentage.
4. **Temperature Coefficient**: This indicates how the capacitance value changes with temperature, which is crucial for applications in varying environmental conditions.
III. Applications of Capacitors
Capacitors are utilized in a wide range of applications, each leveraging their unique properties:
A. Power Supply Circuits
In power supply circuits, capacitors are used for smoothing and filtering. They help to reduce voltage fluctuations and provide a stable output voltage. Additionally, they store energy, allowing for a more consistent power supply during transient loads.
B. Timing Circuits
Capacitors play a vital role in timing circuits, such as oscillators and delay circuits. By charging and discharging at specific rates, capacitors help control the timing of signals, which is essential in applications like clocks and timers.
C. Signal Coupling and Decoupling
In audio and radio frequency (RF) applications, capacitors are used for signal coupling and decoupling. They allow AC signals to pass while blocking DC components, ensuring that signals are transmitted without distortion.
D. Motor Starters and Control Circuits
Capacitors are also used in motor starters and control circuits. They provide the necessary phase shift to start single-phase motors and help in controlling the speed and torque of electric motors.
E. Energy Storage in Renewable Energy Systems
With the rise of renewable energy systems, capacitors are increasingly used for energy storage. They can quickly store and release energy, making them ideal for applications like solar power systems and electric vehicles.
IV. Capacitor Products in the Market
A. Overview of Capacitor Manufacturers
The market for capacitors is vast, with numerous manufacturers producing a wide range of products. Companies like Murata, Vishay, KEMET, and Nichicon are well-known for their high-quality capacitors used in various applications.
B. Popular Capacitor Products
Capacitors are found in numerous products across different sectors:
1. **Consumer Electronics**: Capacitors are integral to devices like smartphones, laptops, and televisions, where they help manage power supply and signal processing.
2. **Industrial Applications**: In industrial settings, capacitors are used in machinery, automation systems, and power distribution networks.
3. **Automotive Applications**: Modern vehicles utilize capacitors in various systems, including engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety features.
C. Emerging Trends in Capacitor Technology
The capacitor industry is evolving, with several emerging trends:
1. **Miniaturization**: As electronic devices become smaller, the demand for compact capacitors is increasing. Manufacturers are developing smaller capacitors without compromising performance.
2. **Increased Capacitance Values**: There is a growing need for capacitors with higher capacitance values to support advanced applications, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
3. **Environmentally Friendly Materials**: With a focus on sustainability, manufacturers are exploring environmentally friendly materials for capacitor production, reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste.
V. Challenges and Considerations
A. Limitations of Capacitors
Despite their advantages, capacitors have limitations:
1. **Voltage Breakdown**: Exceeding the voltage rating can lead to breakdown and failure, which can damage circuits.
2. **Leakage Current**: Capacitors can experience leakage current, which can affect performance, especially in precision applications.
B. Selecting the Right Capacitor for an Application
Choosing the right capacitor requires a thorough understanding of application requirements. Evaluating specifications such as capacitance, voltage rating, and tolerance is crucial to ensure optimal performance.
C. Future Developments in Capacitor Technology
The future of capacitor technology looks promising, with ongoing research focused on improving performance, increasing energy density, and developing new materials. Innovations in nanotechnology and organic materials may lead to the next generation of capacitors with enhanced capabilities.
VI. Conclusion
Capacitors are indispensable components in modern electronics, playing a vital role in various applications. Their ability to store and release electrical energy makes them essential for power supply stabilization, timing circuits, signal processing, and energy storage in renewable systems. As technology continues to evolve, capacitors will remain at the forefront, adapting to new challenges and opportunities. Understanding the different types of capacitors, their applications, and the latest trends will empower engineers and enthusiasts alike to make informed decisions in their projects and designs.
VII. References
For further reading and resources on capacitors, consider exploring the following:
- "Capacitors: Principles and Applications" by John Smith
- "The Art of Electronics" by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill
- Industry standards and guidelines from organizations like the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
By delving deeper into the world of capacitors, one can appreciate their significance and the innovations that continue to shape the future of electronics.